Some people may not understand the cowpea, because most of the areas are called cowpeas. Because of the green and healthy life that people are now pursuing, green vegetables are becoming more and more popular. Let’s explain the harmlessness of cowpeas. Production technical specifications.
1.1 Seed treatment
1.1.1 Selection
Seed selection prior to sowing, removing seed, mold and damaged seeds.
1.1.2 Sunning
The selected seeds are air-dried for 1d to 2d.
1.1.3 Seed disinfection
Seed dressing with 50% carbendazim WP of 0.5% seed quality to control blight and anthracnose; or soaking seeds with 500 times solution of streptomycin sulfate, the soaking time is controlled within 4 hours to control bacterial diseases.
1.1.4 Soaking seeds and germination
The seeds after drying are soaked in warm water of 45 ° C, the soaking time is controlled within 4 hours, and the germination is carried out at 25 to 28 ° C for 1 to 2 days, and the seeds can be sown when 50% of the seeds are white.
1.2 seed quantity
The cultivated area per 667 m2 is dwarf type: 8-10 kg, and vine type 4-6 kg.
1.3 Open field broadcast
1.3.1 Geothermal requirements
When the ground is broadcast live, the ground temperature of 10cm should be stable at 15 °C; when the facility is cultivated, the ground temperature of 10cm should be stable at 12 °C.
1.3.2 Seeding method
Ditch or open a hole on the cultivation pot, carry out on-demand, and soak 3 to 4 dried seeds per hole, and soak the depth 2cm~3cm.
1.4 facility nursery
In order to mention the morning market, seedling transplanting methods should be adopted. The nursery facilities and substrate should be disinfected. The seedlings are incubated with nutrient clams of 6cm to 8cm in diameter or 8cm×8cm, and the seeds after soaking are spotted in nutrient or nutrient blocks, and 2 to 3 grains per loach. Before sowing, the nutrient meal (block) should be watered, sowed 2cm ~ 3cm, and then covered with soil 2-3cm.
1.5 Seedling management
1.5.1 Temperature Management
Cowpea seed germination optimum temperature 25 ° C ~ 30 ° C, the lowest temperature 10 ° C ~ 12 ° C
Live broadcast: After the early cultivation of spring, the mulch or small arch shed should be covered in time to facilitate the emergence of seedlings. When 30% of the seeds are unearthed, the mulch or the shed should be removed.
Seedling: After sowing, the temperature in the nursery facility is 25°C~30°C during the day and 16°C~18°C at night; after emergence, the daytime temperature is 20°C~25°C, nighttime 15°C~16°C; 4d~5d before planting, the temperature is lowered. Seedlings, daytime temperature 20 ° C ~ 23 ° C, night 10 ° C ~ 16 ° C.
1.5.2 Water and fertilizer management
In the seedling stage, the cultivating should be strengthened, and after the seedlings are released, a cultivating will be carried out, and the stalks will be ploughed 2 times to 3 times in combination with the watering. The seedling stage should be based on water control and fertilizer control.
1.6 Strong seedling standards
The calendar is 20 to 25 days old, the physiological seedling age is about 20 cm in height, the development degree is about 25 cm, the stem is 0.3 cm or less, and the true leaves are 3 to 4 pieces. The root system is developed and there are no pests and diseases.
2, soil preparation and fertilization
2.1 Fertilization principle
Fertilizer application should be in accordance with NY/T 496-2010. It is forbidden to use chemical fertilizers and biological fertilizers and organic fertilizers that have not been registered by the national or provincial agricultural departments, and do not use fertilizers that have not been safely tested and organic fertilizers and mineral fertilizers that have excessive levels of heavy metals. Industrial waste and municipal and organic fertilizers that do not meet pollution-free targets are not used.
2.2 Base fertilizer application rate
After the harvest of the former crops, the pasture should be cleaned as early as possible, and 6,000 kg to 5000 kg of decomposed organic fertilizer should be applied per 667 m2, 20 kg to 40 kg of superphosphate, 50 kg to 10 kg of potassium sulfate as the base fertilizer, and 25 cm to 30 cm deep, and then the soil was dried and the soil was dry. Watering should be done in advance.

3, colonization
3.1 Planting density
Open field spring and summer and facility spring early cultivation:
Dwarf cowpea: 4000 holes / 667m2 ~ 4500 holes / 667m2
Vine-type cowpea: 3000 points / 667m2 ~ 3500 points / 667m2;
Open field summer and autumn, facilities autumn delay and winter spring cultivation
Dwarf cowpea: 4500 holes / 667m2 ~ 5000 points / 667m2
Vine-type cowpea: 3500 holes / 667m2 ~ 4500 holes / 667m2
The line spacing is 50cm~60cm, the hole distance is 20cm~30cm, and 2 to 3 strains are fixed for each hole.
3.2 Colonization method
Dig a hole in the cultivation hoe, move the seedling with the nutrient soil into the hole, and then plant the seedling water after the planting, and cover the soil after the water seepage. The facility should be covered with mulch for early spring or winter and spring cultivation.
4. Field management
4.1 Temperature Management
The growth temperature of cowpea is 20 °C ~ 30 °C, and the optimum temperature during flowering is 25 °C ~ 28 °C. Indoor cultivation temperature during planting period is 28°C~30°C during the day, 15°C~18°C during the night; 23°C~27°C during the day of the vine, 11°C~14°C during the night; 25°C~30°C during the flowering and podming period, nighttime 15 ° C ~ 18 ° C.
4.2 Lighting Management
A weather-resistant functional film with good light transmission should be used to keep the film surface clean, and shading and cooling measures should be taken in the summer and autumn high temperature seasons.
4.3 Air humidity
According to the requirements of humidity and the need to control diseases in different growth stages of cowpea, the optimal relative humidity of air should be kept at 65%-75%.
4.4 Fertilizer management
4.4.1 The total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in the total growth period of cowpea is required to be nitrogen (N) 12kg~14kg, phosphorus (P2O5) 5kg~6kg and potassium (K2O) 13kg~14kg. Root fertilization should be based on the growth of cowpea and the length of growth period. According to the provisions of NY/T496-2010, balance fertilization to achieve maximum benefits. Watering should be done by drip irrigation or dark irrigation under the membrane.
4.4.2 Before the vines are inserted, the dwarf cowpeas are topped with fertilizer before flowering; the pods are topped for 1 to 2 times. Open shallow trenches between rows or between holes, apply 20kg ~ 30kg of ammonium sulfate per 667m2, 5kg ~ 10kg of potassium sulfate or 20kg ~ 25kg of compound fertilizer. Watering should be carried out according to the soil moisture and with the top dressing. Watering should be controlled after the seedlings or slow seedlings are not watered. The first inflorescence should be filled with water after the pods, and the soil should be kept moist during the pod-forming period.
4.5 Inserts
After the vines are vines, they should be inserted into the racks or slings in time. When the main vine grows to 2m in the open field, the heart is picked, and the main vine grows to 1.5m when it is grown in a plastic greenhouse or a solar greenhouse.
5. Pest control
5.1 Main pests and diseases
Blight, coal mold, rust, powdery mildew, viral disease, underground pests, whitefly, white bean, American spotted fly, aphid, spider mites, noctuid larvae.
5.2 Principles of Prevention
Guided by the principle of “prevention first, comprehensive managementâ€, we should give priority to the use of agricultural, physical, biological, ecological and other control measures from the entire ecosystem, and appropriately use chemical control measures to create harmful diseases that are not conducive to pests and diseases, etc. The environmental conditions in which natural enemies proliferate maintain the balance of the vegetable field ecosystem and the diversity of the organism, control the pests below the allowable economic threshold, and reduce the pesticide residues to the prescribed standards.
5.3 Agricultural measures
5.3.1 Rotation for rotation, and rotation with non-bean crops for more than 3 years.
5.3.2 Clean up the garden, clean up the diseased leaves, fallen leaves and weeds, and keep the fields clean.
5.4 Physical control
5.4.1 Facility cultivation, closed with insect nets at the air outlet. In summer, it is covered with plastic film and insect-proof net (≥40 mesh) for rain, sun and insect-proof cultivation.
5.4.2 Hang yellow boards in the facility to trap pests such as aphids and whitefly.
5.4.3 Use a silver-coated mulch or a silver-gray film strip to avoid smashing.
5.4.4 Use frequency-vibration insecticidal lamps and black light lamps to trap pests such as adult beetles and beet armyworms.
5.5 Biological control
5.5.1 Actively protect and use natural enemies to prevent pests and diseases. Selective insecticides are used to protect and use natural enemies, to control the hazards of pests and diseases, and to cultivate the plants. The Lizard bee can be released to control the whitefly, and when the whitefly is found to be adult, the bee card can be started. Generally, the amount of bee per acre is not less than 10,000.
5.5.2 Using biological agents to control pests and diseases Use 1% agricultural anti-wuyinmycin 150 times to 200 times liquid to control gray mold and powdery mildew. Control the bacterial disease with 1 million units of neo-phytomycin powder 3000 times to 4000 times. The leafhopper and the Liriomyza sativae were controlled with 1.8% avermectin EC 3000 times to 5000 times.
5.6 Chemical control
Kidney bean easy to exceed the standard agent: amphetamine
According to the provisions of GB 4285, GB/T 8321 and NY/T1276-2007, rational use of drugs (see Table 1); strict control of the safe interval of pesticide use.
Table 1 Main pests and diseases of cowpea at different growth stages and its control measures
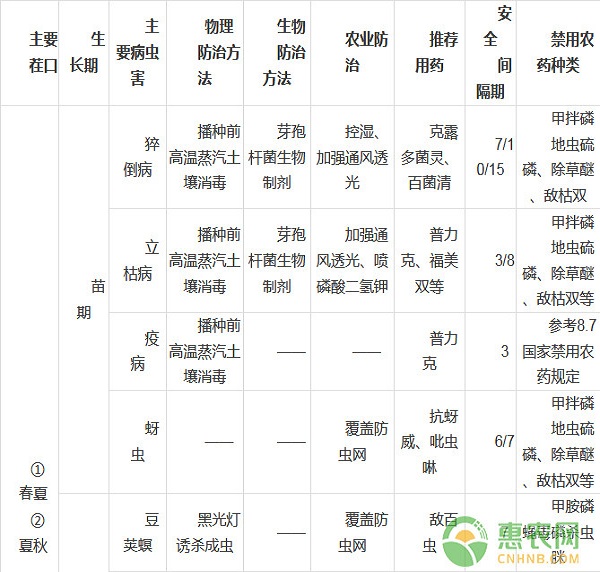



6, harvest
The cowpea pods grow to the standard length, the pods are soft and full, and the seeds are not harvested when the seeds are not significantly expanded. It is harvested once in the initial period of harvesting from 3d to 5d, and harvested once in the period from 2d to 3d.
The above is all about today's cowpeas. Welcome the needy farmers to come to Huinong.com, Xiaobian reminds everyone to download the mobile Huinong app to watch the latest Sannong information anytime, anywhere!
Thoracoscopic Scissor,Thoracoscopic Instruments Forceps,Thoracoscopic Instruments Straight,Vats Curved Scissors
ZHEJIANG SHENDASIAO MEDICAL INSTRUMENT CO.,LTD. , https://www.sdsmedtools.com