What are the common pests and diseases during the cultivation of green onions? This article mainly talks about the fourteen most common pests and diseases of green onions. Start with the disease of green onion and control the problem of green onion pests. If you need it, you can read the inquiry!

First, onion disease
Onion rust
symptom
Mainly harmful to onion leaves.
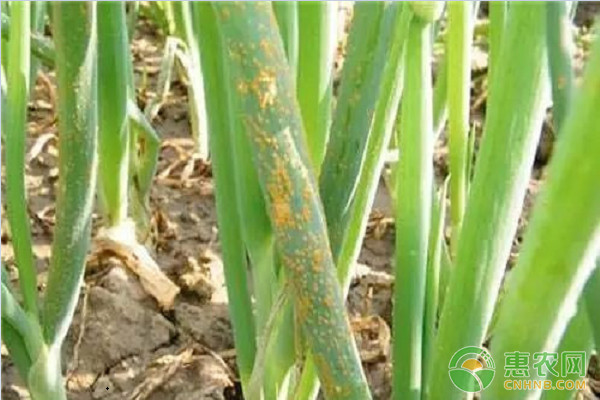

In the early stage, sporadic small bubble spots appear on the leaves, and the development develops a round, elliptical or fusiform small spot. After the epidermis of the lesion is cracked, an orange-yellow or purple-brown powder is scattered.
In severe cases, the onion leaves are covered with scars left after the rupture of the disease, which is easy to die and rot.
Prevention
Spray triadimefon, diniconazole, etc. in the early stage of the disease, and spray the drug once every 10 days for 2 to 3 times.
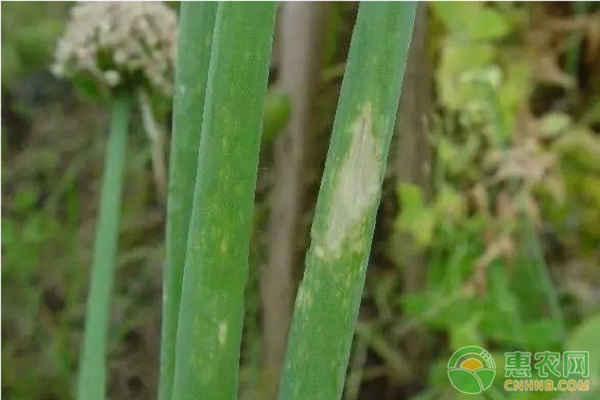

2. Downy mildew
symptom
Mainly harmful to leaves and pedicels.
The leaves are infected and initially produce yellow-white or milky yellow lesions on the leaves, which are spindle-shaped or elliptical. The leaves above the site of the disease are drooping.
After the early onset of the pseudostem, the upper part of the growth is unbalanced, causing the plant to bend toward the victim side. Late onset, the disease is prone to cracking, affecting seed maturity.
When the peduncle is onset, the elliptical lesions appear at the beginning, which are larger, milky yellow, and later turn pale yellow or dark purple.
When the humidity is high, the surface of the lesion is covered with gray fluff. After the bacteria are produced on the lesion, a layer of black velvet mold is sometimes formed.
Prevention
Drug selection: downy mild acid hydrochloride, chlorothalonil, mancozeb, enoyl manganese zinc, frost urea, manganese zinc, aluminum triethylphosphonate, etc., spray once every 5~7 days, continuous 3~ 4 times.
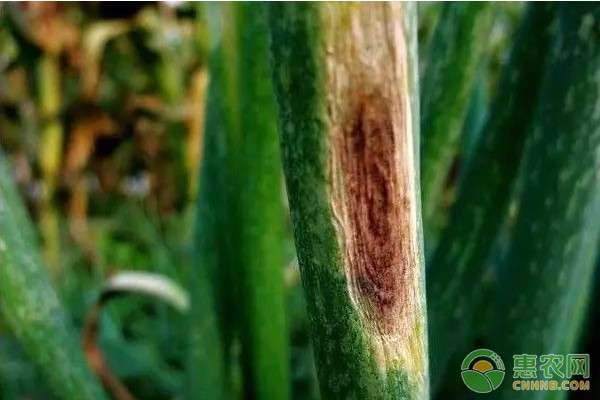

3. Purple spot disease
symptom
Mainly harmful to leaves and pedicels.
At the beginning of the disease, there were water-stained white spots, and the lesions rapidly expanded into spindle-shaped depressions, first pale brown, then brown to blue-purple, surrounded by a yellow halo.
Since then, some gradually faded to form a concentric pattern, and when the humidity is high, dark brown coal powdery mildew is produced on the surface.
If the lesion expands around the leaf or peduncle, it can be broken from the lesion.
Prevention
Pharmacy selection: chlorothalonil, ecstasy • manganese zinc, nail cream • manganese zinc, prochloraz, difenoconazole, etc., spray every 7 to 10 days, for 3 to 4 times.
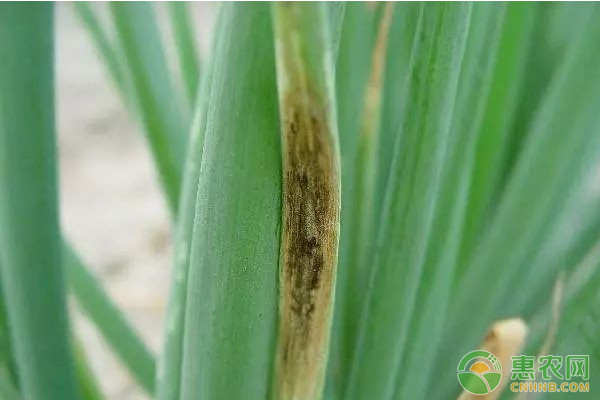

4. Black spot
symptom
Mainly harmful to leaves and stems.
The lesion is initially yellow-white, oblong, and then rapidly expands upwards and downwards. The color changes to dark brown, the edge has a yellow halo, the lesion has a slight ring pattern, and the thick black lint layer grows on the lesion. When the condition is serious, the leaves turn yellow and die.
Prevention
Drug selection: iprodione, eclipse • manganese zinc, chlorothalonil, etc., spray once every 10 days, for 2 to 3 times.
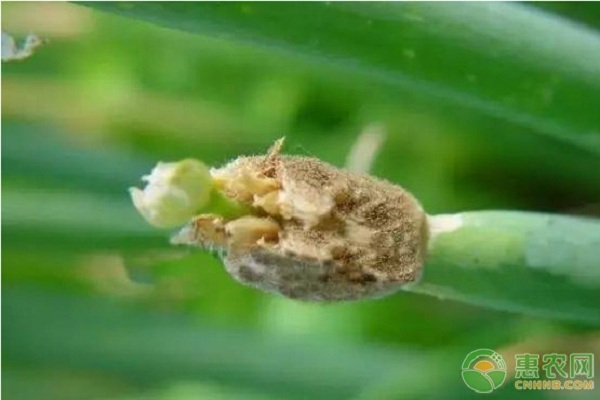

5. Gray mold
symptom
Mainly harmful to the leaves. In the early stage, white spots are produced, and the spots are fusiform to long oval. When the lesions are often collected, they form plaques, causing the half leaves or whole leaves to curl and dry.
When wet, a large number of gray mold layers on the dead leaves, mostly developed from the tip of the leaves, gradually connected into pieces, so that the onion leaves curled and died.
Prevention
Drug selection: procymidone, iprodione, eclipse • manganese zinc, chlorothalonil, pyrimethanil, etc., every 10 days, for 2 to 3 times.
6. Black mold
symptom
Mainly harmful to leaves and pedicels.
The leaves are infected, and there are chlorotic long-spotted spots, which are initially yellowish white and rapidly expand up and down to become dark brown. The edge has a yellow halo, the condition is extended, and the plaque and the plaque can still maintain an elliptical shape, and the lesion has a slightly rounded pattern with distinct layers.
On the late lesions, the dense black short layer, the severely affected leaves turn yellow or die or the stem is broken.
Prevention
Pharmacy selection: Benseson zinc, captan, pyraclostrobin, iprodione, myclobutanil, etc., spray once every 5 to 7 days.
7. Soft rot
symptom
When the bulbs are inflated, the translucent gray-white lesions are produced in the lower part of the 1~2 outer leaves. The base of the leaf sheath softens and rots, the outer leaves fold down, and the lesions expand downward.
The initial stage of the pseudo-stem was water-stained, and the inside began to rot, emitting a stench.
Prevention
Agent selection: acacia copper, copper hydroxide, agricultural streptomycin, etc., every 7 to 10 days, for 2 to 3 times.
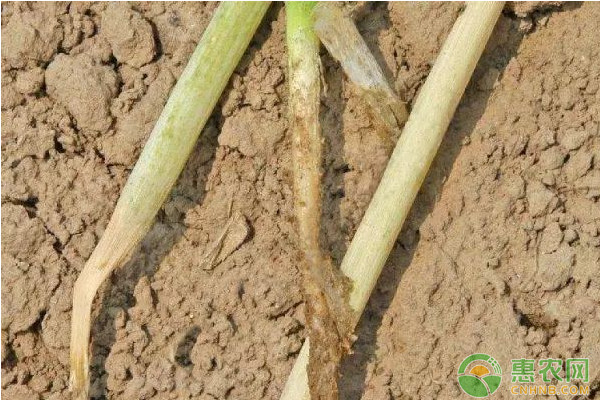

8. White rot
symptom
At the beginning of the disease, the tip of the outer leaf is strip-shaped, or the tip of the leaf gradually turns yellow, and then spreads to the leaf sheath and the inner leaf. The growth of the plant is weak, and the whole plant turns yellow and die when it is severe.
When the diseased plant was pulled out, the epidermis of the bulb was stained with water stains, the base of the stem became soft, and the bulb became black and rot.
Prevention
Drug selection: carbendazim, thiophanate-methyl, iprodione and the like.
9. Disease
symptom
Mainly harmful to the leaves.
When the lesion spreads to half of the leaf, it is wet and rot, and causes the onion to droop. The affected part is yellow and dry, leaving only two layers of membranous skin. The dead part of the seriously ill field often reaches half of the length of the onion tube, or even 2/3.
After the stem is damaged, the root plate is watery, light brown to dark green.
The root is damaged, the root hair is less, and it becomes brown and rot.
When the humidity is high, the disease minister has a white sparse mold layer.
Prevention
Pharmacy selection: nail cream manganese zinc, chlorfenapyr hydrochloride, enoyl propyl zinc, pyraclostrobin, etc., spray every 7 to 10 days, for 2 to 3 times.
10. Small sclerotinia
symptom
Mainly harmful to leaves and pedicels.
In the early stage of the disease, the tip of the leaf or pedicel is discolored first, and gradually expands downward, causing the onion strain to partially or completely die, leaving only new leaves.
Peeling the diseased leaves, visible white cotton-like hyphae, scattered yellow-brown or black sclerotia under the epidermis.
Prevention
Drug selection: carbendazim, thiophanate-methyl, iprodione, etc., every 7 to 10 days, for 2 to 3 times.
11. Viral disease
symptom
The new leaves of the diseased plant are thin, the leaves are light, the yellow leaves appear on the new leaves, the leaves are uneven, the leaves are yellow, and the yellow-green mottled or yellow strips on the leaves are spirally twisted. The sag becomes yellow, and some leaves are twisted to one side, and the plants shrink.
Prevention
Agent selection: morpholinium hydrochloride (passivation virus) + pymetrozine (killing poisoning pests) + mushroom polysaccharides (improving resistance). Other recipes with similar functions are also available.
Second, pests
Leaf miner
Hazard characteristics
The plants that are harmed are: the larvae drill on the leaves and sheaths of the onions to eat the mesophyll and epidermis, and form gray-white irregular squats. The larvae drill in the stalks throughout the onion leaves, endangering the veins. Will cause the tops of the green onions to die dry.
Morphological characteristics
The larvae are pale yellow, slender and cylindrical, with a pair of posterior valve protrusions on the back of the tail; the wall is translucent, green, and the internal organs are faintly visible from the outside.
Prevention
The damaged leaves were found to be removed at any time and concentrated for burial. After the harvest is completed, the plant residues and weeds in the field are completely removed in time.
When the larvae start to harm, timely control with avermectin, beta-cypermethrin, etc.
2. Onion horse
Hazard characteristics
Adults and nymphs use the frustration mouthparts to damage the heart leaves and buds of the host plants, causing the leaves of the host to form many long yellow-white or gray-white markings, and the leaves are twisted and deformed.
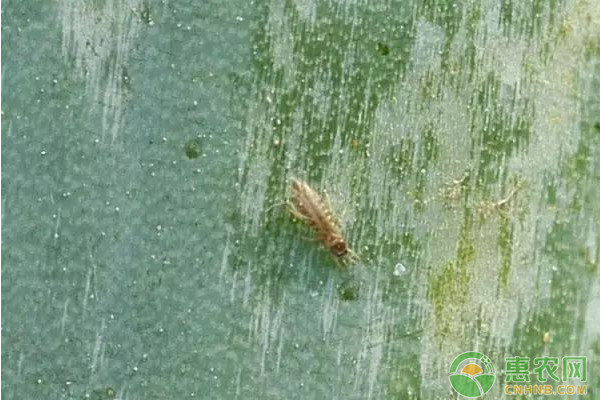

To damage the leaves, the leaves are sucked to form white spots. In severe cases, the whole leaves are grayish white due to chlorosis.
Morphological characteristics
The adult locusts are 1.2 to 1.4 mm long, light brown, and have an antennae of 7 knots. The wings are long and narrow, the veins are sparse, and the edges of the hind wings have many slender manes.
There are 9 black abdomen on the sides of the abdomen and abdomen. There are several long black bristles in the last section of the abdomen.
The male oviduct is saw-shaped and long. The male is wingless. Egg-shaped kidney, 0.29 mm long, milky white.
Late oval, yellow-white, visible red eye points. Shiny.
The nymphs are 4 years old, the whole is yellowish, the tentacles are 6 knots, and the fourth section has 3 rows of micro-hairs. There are fine points on the chest and abdomen, and there are thick hairs on the points.
Prevention
(1) Agricultural control
Remove the weeds and residual leaves in the field, concentrate on burning or deep burial, and eliminate the overwintering insects.
Strengthen the management of fertilizer and water to promote the robust growth of plants.
(2) Chemical control
Sprays such as spirotetramat, nitenpyram, flonicamid, and zhongdingwei are used.
Onion fly
(green onion, garlic chop)
Hazard characteristics
It is mainly caused by larval damage, and the larvae are harmful from the seedling stage, causing erosion of the bulbs and causing decay. And caused the upper leaves to wither and even withered.
Morphological characteristics
The larvae are scorpion-like, and the mature larvae are 9 to 10 mm long and milky white. There are 7 pairs of protrusions in the abdomen tail section, both of which are not bifurcated, the first pair is higher than the second pair, and the sixth pair is significantly larger than the fifth pair.
Prevention
The newly hatched larvae and adults can be sprayed with fipronil, avermectin, chlorfenapyr, and beta-cypermethrin.
About the common pests and diseases of green onions and their prevention and treatment methods Today, the vegetable farmers who need it can continue to pay attention to Hui Nongwang!
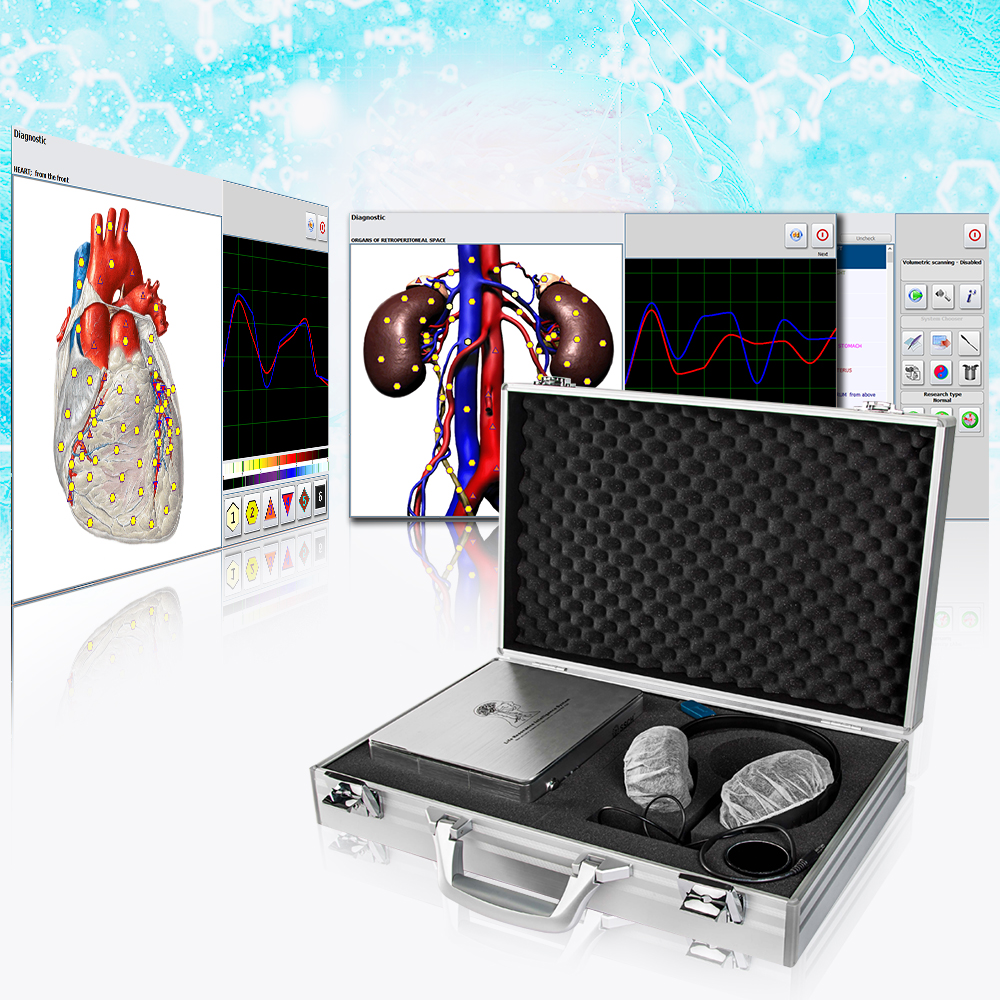
Metatron Hunter 4025
Metatron Hunter 4025,Metapathia Gr Hunter 4025,Metatron 4025 Nls,Metatron Gr Hunter 4025,Vector V16,Vector V19
The NLS Metatron Hunter 4025 machine is a bioresonance diagnostic and therapy device. It is based on the principles of quantum physics and uses the concept of resonance to assess the health status of an individual. The machine utilizes electromagnetic waves to scan the body and provide information about the functioning of various organs, tissues, and systems. It can detect imbalances, pathogens, and other factors that may contribute to health issues. The Metatron Hunter 4025 machine can also provide therapy by applying specific frequencies to restore balance and promote healing. It is used by some practitioners as a complementary tool for health assessment and treatment.
The Metapathia-GR Hunter software can operate only with the telemetric nonlinear analysis data processing apparatus "Metatron" and its subsequent modifications. The telemetric nonlinear analysis data processing device is compatible with the IBM-type PCs and intended for studying reaction of a biological object to different types of the informational impact. "Metatron" allows correlating the measurement process with the process affecting it and performs the following.
Metatron Hunter 4025,Metapathia Gr Hunter 4025,Metatron 4025 Nls,Metatron Gr Hunter 4025,Vector V16,Vector V19
Shenzhen Guangyang Zhongkang Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szlighttherapymachine.com