Release date: 2015-09-29
Artificial intelligence is used to increase the efficiency and automation of health care services. The development of artificial intelligence technology has been questioned in the past, and now we find that big data technology is advancing the process of artificial intelligence, as well as in the medical and health field. Take a look at the following advancement of artificial intelligence applications with the arterial network.
Analyze patient behavior and develop a personalized cancer treatment plan
For example, two breast cancer patients may get the same treatment plan, but the physical condition of the two may be completely different.
One of them may be a marathon runner, the other is a person who likes to read quietly; one may be a smoker, the other may be a health-conscious person; one may be in his 60s and the other just 40. This situation is common around us.
So considering all aspects, these two patients need two different treatment options.
For scientists and doctors, the difficulty lies in grasping the personal information of a particular patient. Important key information is often submerged in large amounts of data, and doctors don't have the time (and probably one year) to filter out what they want in their messages.
So many researchers have tried to use artificial intelligence to overcome this difficulty.
For example, scientists at Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh are using artificial intelligence to select useful information from electronic medical records, diagnostic imaging, prescriptions, genomic data, insurance records, and even wearable devices for specific diseases and special populations. Establish a health care program.
Researchers use big data to create specific medical solutions, control infectious diseases, and find treatments for deadly diseases.

“The biggest problem now is that the system is not smart,†says Eric Xing, a professor of machine learning at Carnegie Mellon University. "Data stored in the system is basically dead data, and machine learning and artificial intelligence can separate useful information from massive data. You can understand that it is like having an artificial brain instead of a 'dead' The storage system is working."
He said Carnegie Mellon University and the University of Pittsburgh are working with the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center on a project called the Pittsburgh Health Data Alliance. In the next six years, the medical center will fund researchers from $10-20 million annually for this study.
Scientists are using health data from medical centers (excluding patient identification information) to study how to analyze big data more quickly and efficiently, to create a health care-related technology and services that can be better for different patients. Diagnosis, treatment and communication.
“Every patient is a different individual,†Xing added. “A very simple point, such as breast cancer, should be treated with drugs A or B. But because of the uniqueness of lifestyle, living environment and other related health factors. That makes everyone a different independent individual. Artificial intelligence is not just about extracting information from a doctor, but from a large number of experienced doctors, so that it can sort out common information from different patients. ."
In addition, artificial intelligence software works much more efficiently than the human brain, enabling faster identification of patterns and similarities in data, helping doctors and scientists discover the most critical information.
For example, a 50-year-old diabetic has a positive lifestyle and a treatment may be effective for him. Then the doctor can use the same treatment to treat other diabetic patients with the same characteristics.
Xing said that their team is working on an app that can provide users with some healthy living advice and avoid some diseases. This app may go live within one year.
Philip Lehman, associate dean of computer science at Carnegie Mellon University, told the author that the app uses artificial intelligence to tell people when to see a doctor, what doctors to consult, and how to stay healthy.
"For example, now everyone usually searches by mobile phone, 'How do I get to somewhere'." Lehman said in an interview. "Actually, it is the same for you to move it to medical treatment. 'What can I do to feel better or live longer?"
Lehman and Xing hope that from App to machine learning tools and services, they will be able to extend the prototype of different products and develop more than a dozen new products in the next 5-6 years.
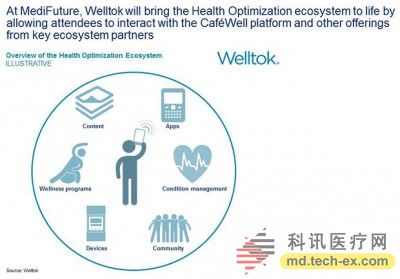
The more famous company in this area is Welltok, which is invested by IBM. It uses IBM's "Watson" supercomputer to build a vision of communicating with users through personalized activities. Its App Cafewell Concierge leverages Watson's natural language processing capabilities to better understand user needs, balance incentives and warnings to users, and deliver back to users with the desired goals.
Virtual medical assistant to improve drug compliance
For example, Aicure uses mobile technology and facial recognition technology to determine whether a patient takes medication on time, then uses the app to obtain patient data, and uses automated algorithms to identify medications and drug intake. Patient data is fed back to the clinician via real-time feedback to the HIPAA (Health Insurance Circulation and Accountability Act) compatible network so that the doctor can confirm if his patient is taking the medication on time. Of course, this technique can also be used to identify adverse events.

There is also an app Alme Health Coach developed by Next IT to find out why people don't take medicine on time. For the health service industry, Next IT is still a newcomer. But it has developed an app "virtual assistant" to help consumers solve problems in banking, retail, property management and so on.
In general, some components of artificial intelligence repeat user utterances to clarify user ideas. Alme Health Coach is specifically designed for specific diseases, drugs and treatments. It can be synchronized with the user's alarm to trigger problems such as 'sleeping well' and can also prompt the user to take the medicine on time. The idea is to collect actionable data available to doctors to better interface with patients (provided patients are willing to share their data).

Track status, automatic reporting support for smart care
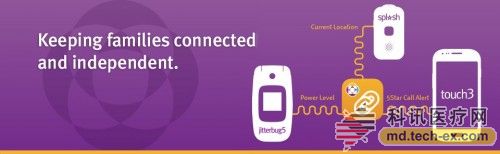
Automated Insights, an artificial intelligence technology company, has partnered with its natural language generation platform, Wordsmith, and Great Call (mobile app developer). Family and friends can get information about the carrier of the device through the GreatCall device connected to the app. It is mainly used for elderly care, when the carrier needs help, the App can receive a message reminder. In addition, the app also has a patented GPS positioning technology that can capture the user's location information.
Currently, the company has been acquired by Vista Equity Partners and STATS (Sports Information Technology). Using Wordsmith's automatic writing function, the caregiver's situation, including location, activity route, battery status, device usage and other information will be automatically generated and reported to the caregiver.
Intelligent drug development
Biotech companies are also combining artificial intelligence and big data to identify new drug compounds, such as Cloud Pharmaceuticals and Berg.
Through the development of the Interrogative Biology artificial intelligence platform, Berg researches human health organizations, explores human molecules and cell defense organizations, and the mechanism of pathogenesis, using artificial intelligence and big data to estimate the potential drug compounds of the human body's own molecules.
This method has many advantages, not only makes targeted therapy a trend in today's medical treatment, but also uses the body's own molecules to treat intractable diseases like diabetes and cancer, which is less than half the time cost and capital of researching new drugs.
Of course, Berg is not the only company in this field. Cloud Pharmaceuticals is focusing on R&D in this area and has raised $20 million.

Also, Johnson & Johnson and Sanofi are also using the Watson super system, a computer system that quickly identifies patterns in massive data, to support drug development.
Johnson & Johnson used "Watson" to quickly analyze the scientific and clinical papers of detailed clinical trial results, speed up the study of the contrast effects of different treatment methods, in order to obtain the application of drugs in a wider range of fields, and these three methods are required by ordinary methods. 10 months to complete these tasks.
Watson now recognizes the chemistry, biology, law, and intellectual property languages, giving scientists the ability to “communicate†with data that others cannot have, which will accelerate breakthroughs in science and medical research.
Sanofi uses Watson to identify other uses of existing drugs, and Watson organizes screening toxicological information to help researchers determine which drugs are more suitable for use in new areas.
Source: Arterial Network
Plant-based protein powders are our hot selling products which can be widely used in sports nutrition and health&wellness fields. Among protein powder from different plant sources, rice protein, pea protein, sunflower seeds protein, pumpkin seeds protein is suitable for making protein bars, protein shakes. Take plant protein as subsititute of animal protein could reduce the risk of getting heart diseases, plant protein contain more fiber and do not contain less healthy compounds found in meat including saturated fat and cholesterol, plant protien are safe and vegan friendly choice.
Plant Protein,Protein Powder,Plant-Based Protein,Rice Protein
YT(Xi'an) Biochem Co., Ltd. , https://www.ytnutra.com